What is Secure Reporting?
Secure reporting is the practice of communicating metrics about security, risk, and performance of security controls to stakeholders. It is essential for security and risk management professionals to provide clear and concise security reports that can drive data-driven decisions and conversations about security and risk.
Important details on cybersecurity threats, hazards in the digital ecosystem, security control gaps, and program performance are provided in a cybersecurity report. Secure reporting can help to measure, manage, and reduce cyber risk, as well as to demonstrate compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Unlocking the Power of Secure Reporting: Navigating Purpose and Scope
Whether you're a business executive, a data analyst, or a cybersecurity enthusiast, understanding the purpose and scope of secure reporting is crucial for maintaining the integrity of sensitive information.
Defining the Purpose of Secure Reporting
At its core, secure reporting serves as a safeguard for confidential data, ensuring that information is shared and accessed only by authorized individuals or entities. In a world where data breaches are a constant threat, the purpose of secure reporting is twofold: to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and to provide a structured means of conveying data insights.
By encrypting, authenticating, and controlling access to reports, secure reporting mitigates the risks associated with data leaks, fostering a climate of trust and reliability among stakeholders.
Navigating the Scope of Secure Reporting
The scope of secure reporting extends far beyond the confines of traditional data protection. It encompasses a comprehensive approach to information security, addressing not only the confidentiality of data but also its integrity and availability.
Secure reporting protocols often involve measures such as access controls, encryption algorithms, and audit trails, creating a layered defense against potential threats. Moreover, the scope of secure reporting extends to compliance requirements, ensuring that organizations adhere to data protection regulations and industry standards.
Understanding the Format: A Blueprint for Secure Reports
The format of secure reporting is akin to a blueprint, outlining the structure and components necessary for safeguarding sensitive information. Reports generated through secure channels typically feature clear categorizations of data, user authentication mechanisms, and encryption algorithms.
Structuring reports in this way not only enhances readability but also ensures that the security measures are seamlessly integrated. Additionally, incorporating watermarking and digital signatures adds an extra layer of authenticity to the reports, reinforcing their trustworthiness.
Unlocking the Structure: The Significance of Report Formats
In the intricate realm of secure reporting, understanding the format is akin to deciphering a blueprint that guides the presentation and communication of critical information.
A well-crafted report format not only enhances the clarity of data but also plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the nuances of report formats, unraveling their significance, and highlighting key considerations for crafting a robust and secure reporting blueprint.
The Essence of Report Format: Beyond Aesthetic Appeal
A report format is not merely a cosmetic feature; it is the structural backbone that shapes how data is conveyed and interpreted. The essence lies in presenting information in a systematic and digestible manner, ensuring that the intended audience can extract meaningful insights effortlessly. The format encompasses the arrangement of data elements, visual components, and the overall design, creating a cohesive narrative that tells a compelling story.
A well-considered report format goes beyond aesthetic appeal; it influences the user experience and aids decision-making. Whether it's financial reports guiding investment strategies or operational reports steering business processes, the format determines how users interact with and comprehend the information presented. Striking the right balance between functionality and visual appeal is essential to create a format that is both effective and engaging.
Components of an Effective Secure Report: Decoding the Blueprint
A comprehensive report format comprises various components, each serving a specific purpose in conveying information accurately and securely. Let's delve into the key elements that form the blueprint of an effective and secure report.
1. Clear Categorization and Structure: Creating Information Hierarchies
At the core of a well-structured report format is the clear categorization and organization of information. This involves creating hierarchies that guide users through the data seamlessly. Headings, subheadings, and a logical flow ensure that readers can navigate the report effortlessly, grasping the context and significance of each section.
Moreover, a well-defined structure enhances readability, making it easier for users to locate specific information. Whether it's a summary at the beginning or detailed sections categorizing data points, the structure creates a roadmap that aids comprehension. In the context of secure reporting, a clear structure also facilitates the implementation of access controls, ensuring that users only access sections relevant to their roles.
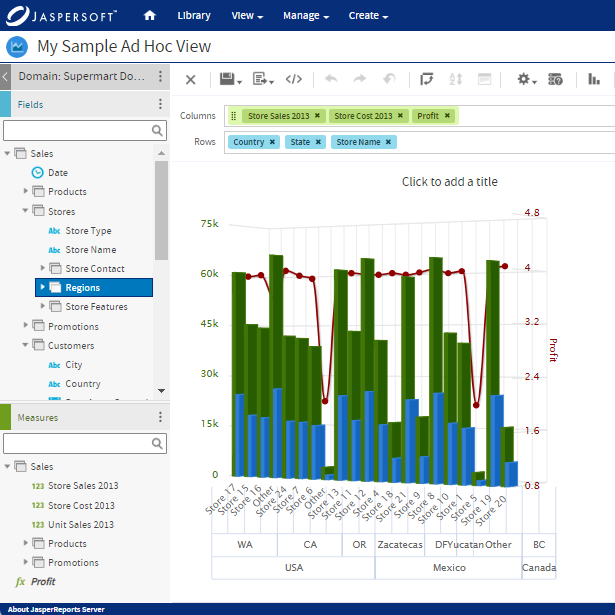
2. Visual Elements: Enhancing Understanding Through Graphics
Visual elements are the unsung heroes of an effective report format. Incorporating charts, graphs, and other visual aids transforms raw data into comprehensible insights. Visual representations not only enhance understanding but also facilitate quicker decision-making by providing a snapshot of trends and patterns.
However, in the realm of secure reporting, the choice and presentation of visual elements require careful consideration. Avoiding overly complex visuals and ensuring that graphs and charts align with the sensitivity of the data being presented is crucial. Striking the right balance between informative visuals and data security is a hallmark of a well-crafted report format.
3. Consistent Formatting: Fostering a Professional Image
Consistency in formatting is a subtle yet impactful aspect of an effective report format. From font choices and color schemes to alignment and spacing, maintaining a uniform appearance fosters a professional image. Consistency extends beyond aesthetics; it influences the perception of reliability and attention to detail.
In the context of secure reporting, consistent formatting also plays a role in reinforcing security measures. A uniform structure aids in the identification of any deviations or anomalies, making it easier to spot potential security breaches. Additionally, it contributes to a seamless integration of security features, such as watermarks or encryption indicators, without compromising the overall visual coherence.
4. Data Encryption and Watermarking: Safeguarding Sensitive Information
The security aspect of a report format goes hand in hand with protecting sensitive information. Incorporating data encryption and watermarking features adds an extra layer of security to the format. Encryption ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains indecipherable without the appropriate decryption keys.
Watermarking, on the other hand, serves as a visible indicator of the report's authenticity. It can include details such as the date of creation, user information, or security classification. This not only acts as a deterrent to unauthorized sharing but also provides a traceable signature, enhancing accountability within the reporting environment.
5. Infrastructure Assessment: Strengthening the Foundation
At the core of secure reporting is the underlying infrastructure that houses sensitive information. Regular assessments of the infrastructure involve evaluating the robustness of servers, databases, and networks. This layer of defense ensures that the foundation of secure reporting is resilient against potential attacks or unauthorized access attempts.
Infrastructure assessments also include the examination of data storage practices. Whether on-premises or in the cloud, evaluating the security protocols governing data storage is crucial. Regular assessments identify any lapses in encryption, access controls, or data retention policies, allowing organizations to fortify the foundation upon which secure reporting relies.
6. Access Controls and Permissions: Limiting Exposure
A crucial layer of defense lies in controlling access to sensitive information. Regular assessments of access controls and permissions involve scrutinizing who has access to what data and what actions they can perform. This layer ensures that only authorized individuals have the necessary privileges, limiting the exposure of sensitive information.
Access control assessments delve into the intricacies of role-based access controls (RBAC), ensuring that users only have access to the data essential for their roles. Regular evaluations validate the alignment of access controls with the organization's evolving structure, guaranteeing that access permissions remain current and in line with security policies.
7. Application Security: Fortifying the User Interface
Secure reporting often involves user interfaces and applications that facilitate the manipulation and presentation of data. Regular security assessments of these applications focus on identifying vulnerabilities, potential exploits, and weaknesses in the code. This layer of defense ensures that the tools used for secure reporting are fortified against potential cyber threats.
Application security assessments extend beyond traditional firewalls. They involve scrutinizing the coding practices, implementing secure coding standards, and conducting penetration testing to simulate real-world attack scenarios. Regular evaluations of application security contribute to the continuous improvement of tools, making them resilient against evolving cyber threats.
8.Safeguarding Trust and Integrity
The benefits of regular security assessments extend far beyond the immediate identification of vulnerabilities. They serve as guardians of trust and integrity within the secure reporting environment. Let's explore the key advantages that organizations gain by embracing a proactive approach to security assessments.
9. Early Detection of Vulnerabilities: Nipping Threats in the Bud
Regular security assessments act as early warning systems, enabling organizations to detect vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. By identifying weaknesses in the security infrastructure or potential points of entry for cyber threats, organizations can proactively address and rectify issues, preventing security breaches before they occur.
This early detection is instrumental in maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information. It allows organizations to stay one step ahead of potential threats, reducing the likelihood of data breaches and instilling confidence in stakeholders that their information is secure.
10. Continuous Improvement: Adapting to Evolving Threats
The landscape of cybersecurity is dynamic, with threats constantly evolving. Regular security assessments contribute to a culture of continuous improvement by adapting security measures to counter emerging threats. Whether it's updating encryption protocols, enhancing access controls, or fortifying application security, these assessments ensure that the security posture evolves in tandem with the changing threat landscape.
Continuous improvement not only enhances the resilience of the secure reporting environment but also demonstrates a commitment to staying abreast of the latest cybersecurity trends. It sends a powerful message to stakeholders that security is not a static concept but an ongoing and evolving effort to safeguard sensitive information.
Challenges in Implementing Secure Reporting
While the benefits of regular security assessments are undeniable, organizations often face challenges in their implementation. Navigating the complexities inherent in conducting assessments requires careful consideration of various factors. Let's explore the common challenges organizations encounter and how to overcome them.
1. Resource Constraints: Balancing Priorities
One of the primary challenges is resource constraints, both in terms of personnel and budget. Organizations may struggle to allocate dedicated resources for regular security assessments, especially if they perceive other operational priorities as more pressing. Balancing these priorities requires a strategic approach that emphasizes the long-term benefits of a secure reporting environment.
Organizations can address resource constraints by leveraging automated tools for certain aspects of security assessments. Automation streamlines the evaluation process, allowing teams to focus on interpreting results and implementing corrective measures. Additionally, emphasizing the return on investment in terms of enhanced security can garner support for allocating resources to regular assessments.
2. Integration with Existing Processes: Ensuring Synergy
Another challenge lies in integrating regular security assessments seamlessly into existing operational processes. Organizations may face resistance if assessments disrupt day-to-day activities or if there is a perceived clash with other business priorities. Ensuring synergy requires a thoughtful approach that aligns security assessments with overall business goals.
Integration can be facilitated by incorporating security assessments into existing change management processes. By viewing assessments as a routine part of organizational evolution, the potential disruption is minimized. Communication and collaboration between security teams and other departments are key to ensuring that assessments enhance overall business objectives without creating friction.

Best Practices in Secure Reporting: A Roadmap to Reliability
Embarking on the journey of secure reporting demands a commitment to best practices that guarantee the highest level of protection. These practices include regular security assessments, staying abreast of evolving encryption standards, and implementing role-based access controls. Training and awareness programs for users also play a pivotal role in fortifying the security chain, ensuring that individuals are well-versed in identifying and responding to potential threats.
1. Implementing Role-Based Access Controls
Role-based access controls (RBAC) lie at the heart of secure reporting best practices. This approach tailors data access permissions based on the roles and responsibilities of individuals within an organization. By granting access only to those who require specific information for their roles, RBAC minimizes the risk of unauthorized access. This practice not only enhances security but also streamlines data management, fostering an environment of efficiency and accountability.
2. Regular Security Assessments: A Proactive Defense Strategy
In the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity, regular security assessments are a cornerstone of maintaining the robustness of secure reporting systems. Conducting periodic audits and vulnerability assessments helps identify potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities in the reporting infrastructure. This proactive approach allows organizations to address security gaps before they can be exploited, fortifying the overall resilience of the system.
3. Staying Abreast of Evolving Encryption Standards
As technology evolves, so do the methods employed by malicious actors seeking unauthorized access to sensitive data. Staying abreast of the latest encryption standards is imperative for secure reporting. Organizations should consistently update their encryption protocols to align with industry best practices. This not only enhances the confidentiality of the data but also ensures compatibility with emerging technologies and compliance requirements.
Training and Awareness Programs: Empowering Users
Even the most advanced secure reporting systems can be compromised if users are not equipped with the knowledge to identify and respond to potential threats. Implementing comprehensive training and awareness programs is a best practice that empowers users to become the first line of defense. Educating individuals on secure practices, recognizing phishing attempts, and emphasizing the importance of password hygiene contribute to creating a culture of security within the organization.
5. Nurturing a Culture of Trust Through Secure Reporting
In the dynamic landscape of data management, secure reporting stands as a beacon of trust, safeguarding sensitive information and fortifying organizational resilience. Understanding the purpose and scope of secure reporting, along with implementing best practices, is not merely a task; it's a commitment to the integrity of data and the trust of stakeholders.
As technology continues to evolve, embracing a culture of security through secure reporting is the key to navigating the complexities of the digital age. By unlocking the power of secure reporting, organizations not only protect their data but also cultivate an environment where trust and reliability flourish.
Conclusion
Secure reporting is a vital aspect of security and risk management. It enables security and risk professionals to communicate the status and performance of security controls, as well as the threats and risks facing the organization, to various stakeholders.
Secure reporting can help to inform decision-making, prioritize actions, allocate resources, and demonstrate compliance. To create effective security reports, security and risk professionals should consider the purpose, scope, format, and best practices of security reporting. They should also use relevant data, metrics, and visualizations to convey the key messages and recommendations.
Secure reporting can help to improve the security posture and resilience of the organization, as well as to foster a culture of security awareness and accountability.
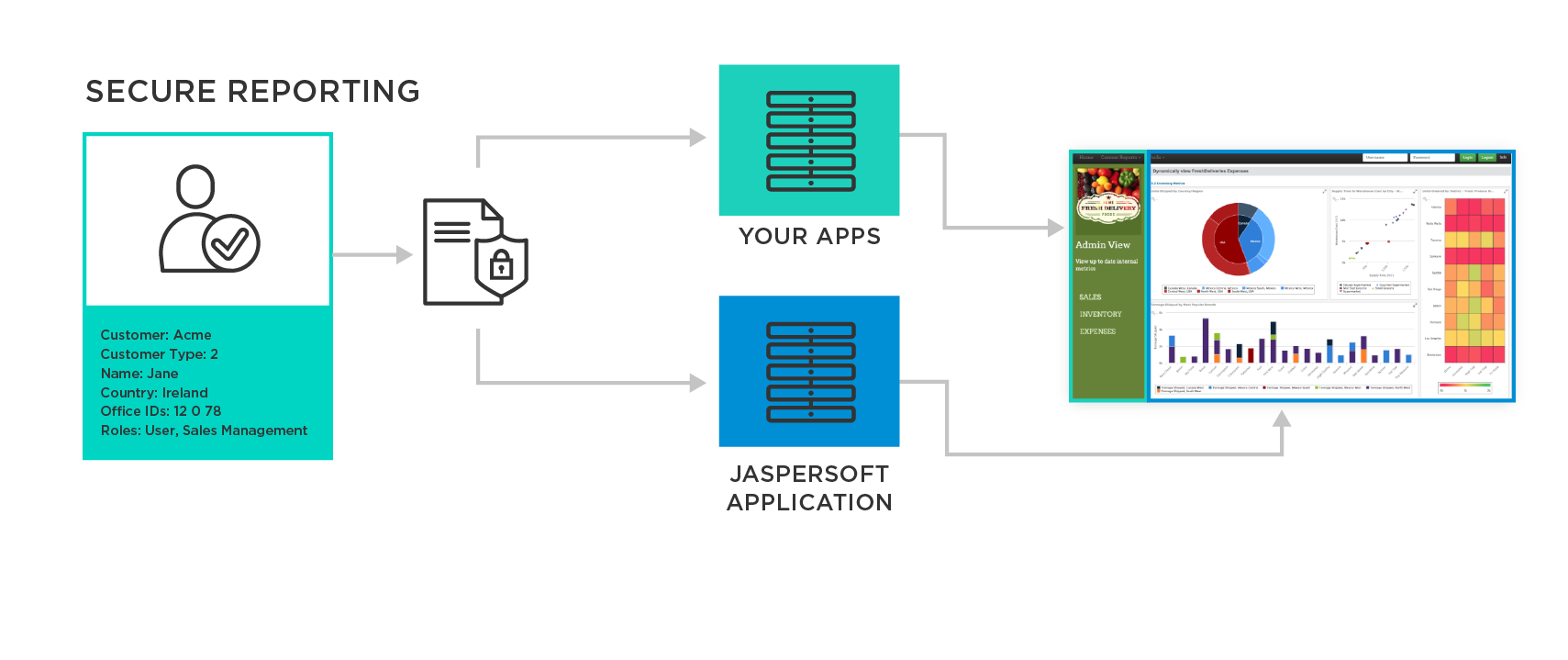
Secure Reporting with Jaspersoft
Related Resources
Jaspersoft in Action: Embedded BI Demo
See everything Jaspersoft has to offer – from creating beautiful data visualizations and dashboards to embedding them into your application.
Ebook: Data as a Feature – a Guide for Product Managers
The best software applications are the ones with high engagement and usage. And those that stick, empower their users to realize the full value of their data. See how you can harness data as a feature in your app.
