What is Cloud Analytics?
Cloud Analytics refers to a service model in which one or more key elements of data analytics are implemented in the cloud. This model can utilize various tools and applications to analyze data, quantify performance, extract and classify business information, and increase the overall efficiency of operations.

Cloud Analytics utilizes various technologies to store and process large data sets, such as Hadoop, Apache Spark, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and SQL Server. Additionally, it includes specialized software for performing advanced analytics operations such as predictive modeling and optimization techniques. It often utilizes powerful visualizations to display the data in visually appealing formats.
Cloud Analytics typically operates on a subscription-based or utility (pay-per-use) pricing model. Offering scalability, accessibility, and flexibility, it enables businesses to handle vast amounts of data while driving insights in real-time. By leveraging AI and machine learning, organizations can quickly discover actionable insights from data-driven decisions.
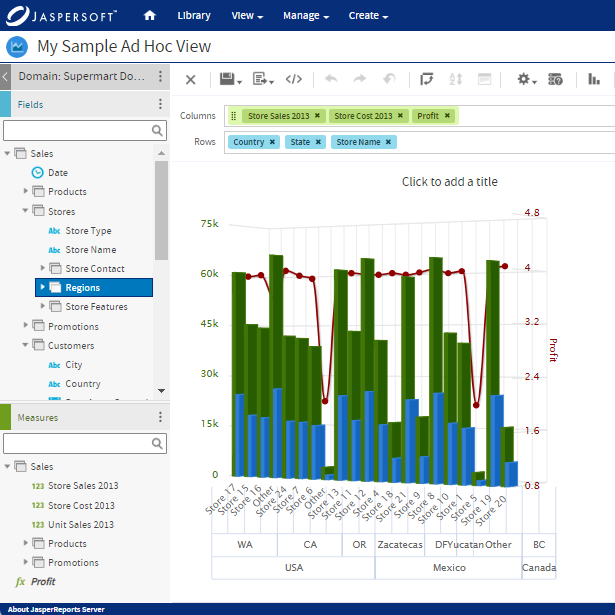
How Do Cloud Analytics Work?
Cloud analytics services work by providing an interface for businesses to access and interact with their data stored in the cloud. This might involve querying the data, developing statistical models, or creating visual presentations for reports. These tasks can be performed using the provided tools and applications designed to handle data processing and analytics tasks efficiently and effectively.
The cloud service provider is responsible for all the necessary infrastructure, software, and hardware needed for cloud analytics. This includes servers, storage systems, data centers, and networking equipment. This relieves businesses of the need to manage these resources themselves, giving them more time and resources to focus on their core operations.
Another key aspect of how cloud analytics works is the integration capabilities it offers. Since the data is stored in the cloud, it can be easily accessed and integrated with other cloud-based applications. These integrations allow for more in-depth and complex analyses, as businesses can pool their data from various sources into a single, unified platform. This leads to more comprehensive insights and helps companies make more informed decisions.
Types of Cloud Analytics
There are three main types of cloud computing and cloud analytics:
Public
Public cloud analytics involves services offered over the public internet and are available to anyone who wishes to purchase them. These services are provided by third-party vendors who manage and control the entire computing infrastructure. The customer has no control over where the infrastructure is located or how it is built.
The primary benefits of this model include cost-efficiency, easy scalability, and high reliability due to the vast network of servers the providers possess.
Private
In a private cloud analytics model, the infrastructure and services are maintained on a private network. These services are usually deployed within the company's intranet or hosted at a data center maintained by the company itself. This model offers a higher level of security and control, which makes it suitable for businesses handling sensitive data or operating in industries with strict compliance requirements.
However, the trade-off is that it can be more expensive and requires a higher level of IT expertise to manage. Private cloud analytics is ideal for businesses that need advanced security, greater customization options, and more control over their data management and analytics.
Hybrid
A hybrid cloud analytics model represents a combination of public and private models. The hybrid model allows data and applications to be shared between them, granting businesses the flexibility to move their workloads between private and public clouds as costs and needs change. This model capitalizes on the benefits of both the public and private models.
It allows businesses to take advantage of the vast resources and scalability of public clouds for non-sensitive operations, while sensitive data can be stored and processed in the private cloud. This two-tier approach provides control and security for sensitive data and the cost efficiency of public cloud usage for other operations, making it an increasingly popular choice among businesses seeking both efficiency and security.
Community
One more significant type of model that merits attention is the community cloud. This is a multi-tenant infrastructure that is shared among several organizations that have common privacy, security, and regulatory considerations. In other words, it's a collaborative system where multiple organizations with similar goals share the infrastructure and related resources.
The cost of setting up and operating the cloud infrastructure, which includes the server, storage, and networking equipment, and accompanying management staff, is spread among the users, thus making it a cost-effective strategy for small to medium-sized enterprises. It also allows these organizations to share and analyze their data in a secure environment, paving the way for collaborative, data-driven decision-making.
Components of Cloud Analytics
The components of cloud analytics include the following:
Data Sources
Data sources in cloud analytics refer to the origins or repositories from which the data to be analyzed is fetched. These could be databases, data warehouses, online spreadsheets, social media feeds, or even real-time sensors and IoT devices. Integration with a diverse array of data sources is a significant advantage of cloud analytics as it allows businesses to draw insights from multiple types of data simultaneously. For instance, a business could blend data from its sales database with customer sentiment data from social media to better understand its customers.
In addition, cloud analytics services often offer connectors to various popular data sources, making it easy to fetch and prepare the data for analysis. They also often support both structured data (such as SQL tables) and unstructured data (like text documents), further enhancing their versatility. These services typically offer robust data management capabilities, including data cleansing, transformation, and integration, which are crucial for preparing the data for analysis and ensuring accurate, reliable results.
Data Models
Data models in cloud analytics provide a structured framework for how data is organized, stored, and retrieved in a database. These models play a critical role in determining how data is interpreted and used for analysis. For instance, an entity-relationship model could be used to understand the associations between different sets of data, while a dimensional model may be employed to analyze data from the perspective of various dimensions, such as time, product, or location.
Moreover, cloud analytics platforms often support multiple data modeling techniques and offer tools for creating custom data models. This allows businesses to design their data models to suit their unique analytical needs and to adapt them as these needs evolve. For instance, a business might use a hierarchical model to analyze organizational data and then switch to a network model for a project involving interconnected data points. With the flexibility provided by cloud analytics, companies can ensure their data models remain relevant and effective, thereby maximizing the value they derive from their data analysis.
Processing Applications
Processing applications form the crux of the analytics system. They are responsible for executing data operations and running analytical tasks. This includes data ingestion, transformation, querying, and visualization. Some processing applications are designed for specific tasks, such as machine learning or statistical analysis, while others are more general-purpose tools that can handle a wide range of analytical operations. Processing applications need to be highly efficient and capable of handling large volumes of data at high speeds. They must also be robust enough to ensure data integrity and security.
In the cloud analytics context, these applications usually utilize distributed computing principles to enhance performance and scalability. They often employ techniques like parallel processing and data partitioning to efficiently manage and analyze large data sets. The choice of processing application is highly dependent on the nature of the business problem, the complexity of the data, and the desired outcomes of the analytics process.
Computing Power
Computing power forms the backbone of any cloud analytics system. It refers to the system's ability to execute commands, perform operations, and process data. In the context of cloud analytics, this often involves running complex algorithms on large data sets. The efficiency, speed, and reliability of these operations are directly dependent on the system's computing power. High computing power is crucial for timely and accurate data analysis, especially when dealing with big data and real-time analytics.
Cloud service providers typically offer scalable computing resources, allowing businesses to adjust their computing power based on their needs. This scalability ensures that businesses have the necessary resources at their disposal at any given time, improving operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
In addition to raw processing power, computing resources in cloud analytics also include storage and networking capabilities. Storage resources determine the volume of data the system can hold, while networking capabilities influence data transfer speeds within the system. Both of these aspects are critical for efficient data management and analytics.
Analytic Models
Analytic models in cloud analytics are mathematical or computational tools used to analyze and interpret data. They are used to uncover patterns, relationships, or trends in the data that can provide meaningful insights to aid decision-making. For example, a business might use a predictive model to forecast future sales based on historical data or a descriptive model to understand the factors influencing customer behavior.
Analytic models can be simple, involving only a few variables, or complex, incorporating numerous variables and sophisticated statistical techniques. The choice of model depends on the nature of the data and the specific questions the business aims to answer. Cloud analytics platforms typically offer a range of built-in models and allow users to create custom models. They also provide tools for model validation, which helps ensure the accuracy and reliability of the insights generated.
Sharing or Storage of Results
Once the data has been analyzed and insights have been generated, the results need to be shared or stored for future use. This is where the cloud shines, as it provides a centralized location for storing and sharing results. Cloud analytics platforms usually offer robust data storage solutions, including data warehouses and databases that are designed to hold large volumes of data. They also provide data governance and security features, such as access controls and encryption, to ensure that the data remains safe and accessible only to authorized users.
Furthermore, cloud analytics platforms promote efficient and collaborative decision-making by allowing analytical results to be shared easily across the organization. Users can create interactive dashboards and reports that visualize the insights in a clear and engaging manner. These dashboards and reports can be accessed from anywhere, at any time, and on any device via the cloud, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the most up-to-date information. Cloud analytics platforms often also support automated report generation and distribution, reducing manual effort and ensuring timely access to insights.
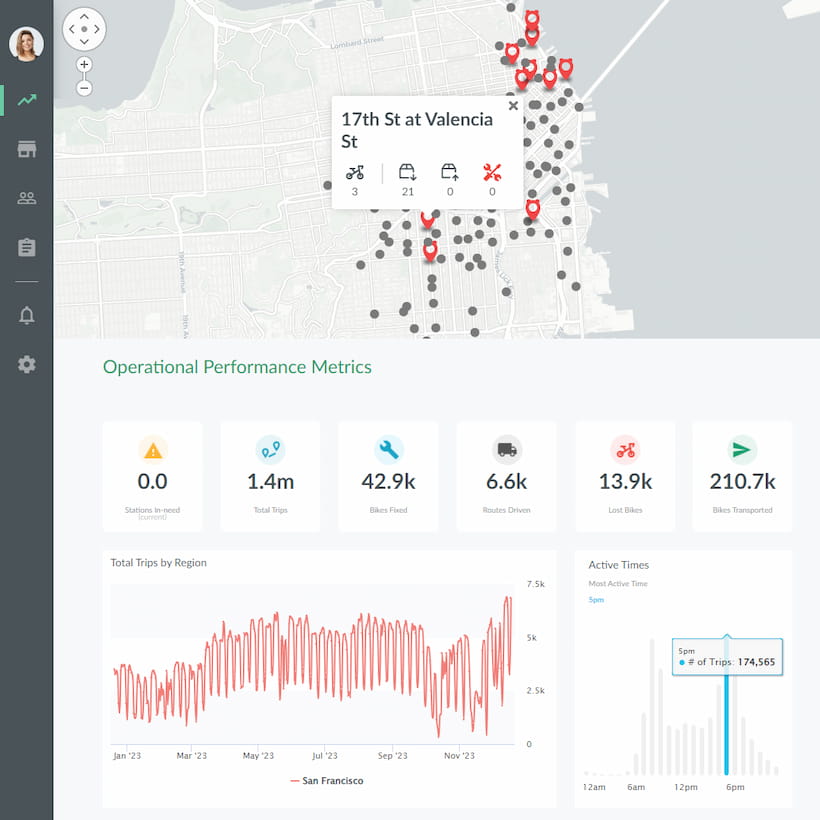
Benefits of Cloud Analytics
The main benefits of using a cloud analytics solution include:
Increased Scalability
Cloud analytics solutions are inherently scalable, allowing organizations to easily adjust their computing resources in line with fluctuating data volumes and analytical needs. This means businesses can start with minimal resources and scale up as their data grows or scale down during off-peak periods. This level of scalability is difficult to achieve with on-premise solutions, which require substantial initial investment and have fixed capacities. With cloud analytics, businesses can operate more efficiently and cost-effectively, as they only pay for the resources they actually use.
Moreover, the scalability of cloud analytics extends beyond just computing resources. It also includes integrating new data sources, incorporating advanced analytical techniques, and supporting increasing numbers of users as the business grows. As such, cloud analytics solutions are scalable in size and capability, making them a flexible and future-proof choice for businesses aiming to leverage data analytics for strategic advantage.
Improved Accessibility
Cloud-based analytics solutions are highly accessible, allowing users to access their data and analytical tools from anywhere, at any time, and on any device. This accessibility is made possible by the nature of the cloud, which stores data and applications on remote servers that can be accessed via the internet.
With a cloud analytics solution, businesses are no longer bound by the limitations of physical infrastructure and can conduct their analytics operations remotely, making it an ideal choice for businesses with distributed teams or those adopting a remote work model. The ease of access also extends to the analytic models and results, which can be shared and collaborated on in real time, improving the speed and efficiency of decision-making processes.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Despite initial concerns about data security in the cloud, modern cloud analytics solutions offer robust security measures that often exceed those of on-premise systems. These measures include advanced encryption techniques for data at rest and in transit, access controls to prevent unauthorized access, and regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. In addition, cloud service providers typically have dedicated security teams that monitor the system round the clock for signs of breaches or attacks.
This commitment to security ensures the data's safety and helps businesses comply with regulatory requirements, such as GDPR and HIPAA, which mandate strict data protection measures. Compliance is further facilitated by features such as automatic updates, which ensure that the system is always up-to-date with the latest security patches and regulatory standards. Thus, by adopting a cloud analytics solution, businesses can enhance their data security and compliance while also freeing up their internal IT resources for more strategic tasks.
Lower Costs
The cost savings associated with cloud analytics come from several sources. Firstly, businesses no longer have to invest in hardware and maintenance for an on-premise solution, reducing the initial capital expenditure. Secondly, they can adjust their computing resources according to demand and only pay for what they actually use, lowering operational costs.
Finally, by outsourcing data storage and management to the cloud provider, businesses can reduce their IT workload and free up internal resources for more strategic tasks. This helps them avoid resource bottlenecks and costly delays while allowing them to shift their focus away from maintenance and toward innovation.
The Challenges in Implementing Cloud Analytics
While the benefits of cloud analytics are numerous, there are also some challenges that businesses should be aware of.
Firstly, choosing the right cloud provider is essential, as different providers offer varying levels of security and support. Therefore, businesses should conduct thorough research to identify a suitable partner that fits their needs and budget.
In addition, it is important to ensure that the cloud analytics solution is properly integrated with existing systems. This requires a deep understanding of the data architecture and analytics processes, as well as an efficient migration strategy. Effectively implemented it can help you solve data accessibility issues when accessing non-cloud resources as well as cloud based data.
Finally, businesses should take into account potential risks such as operational downtime and data breaches when using cloud-based solutions. They can do this by designing effective security protocols and ensuring their cloud provider has a robust backup and recovery system in place.
Cloud Analytics with Jaspersoft
Related Resources
Jaspersoft in Action: Embedded BI Demo
See everything Jaspersoft has to offer – from creating beautiful data visualizations and dashboards to embedding them into your application.
Ebook: Data as a Feature – a Guide for Product Managers
The best software applications are the ones with high engagement and usage. And those that stick, empower their users to realize the full value of their data. See how you can harness data as a feature in your app.
