What is Custom Reporting?
Custom reporting is the process of generating tailored reports designed to meet specific data analysis requirements. In essence, it involves the configuration and creation of reports that precisely align with the informational needs of businesses, researchers, or individuals.
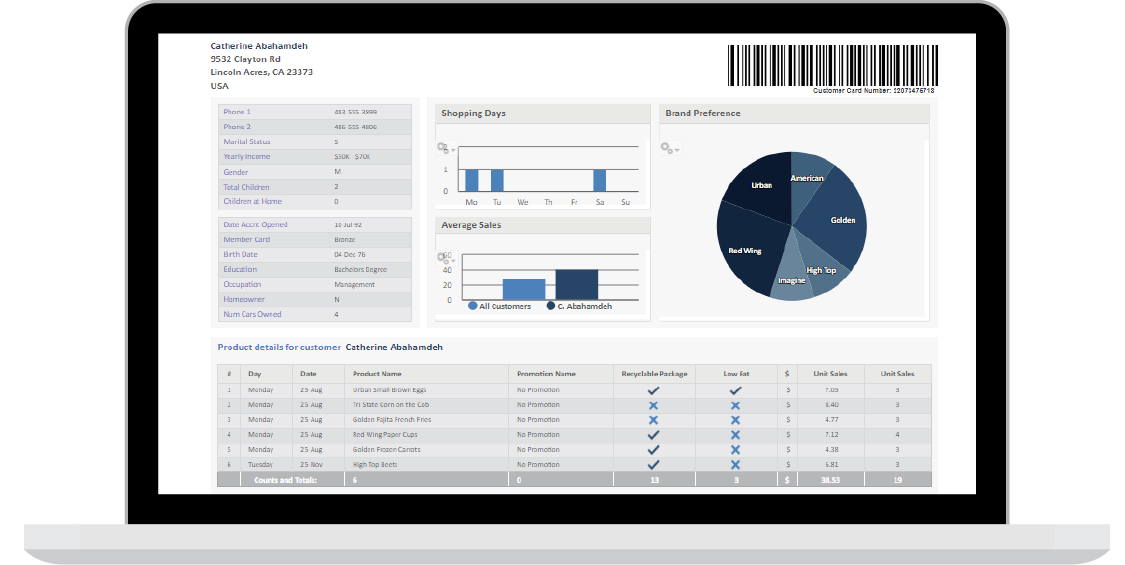
This approach to reporting empowers users to extract targeted insights, emphasizing key metrics, trends, and performance indicators relevant to their analytical objectives. As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow, custom reporting stands as an indispensable tool for transforming raw information into actionable intelligence, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic analysis.
This page takes a closer look at what is custom reporting, expressing its definition, functionalities, applications, and the different reports that can be used within. Custom reporting, in essence, helps user unlock the potential to transform raw data into actionable intelligence, fostering a more informed and approach to data analysis.
Understanding The Concept of Custom Reporting
Custom reporting, at its core, involves the creation and configuration of reports tailored to the specific needs and requirements of users. Unlike standardized or pre-built reports, custom reporting allows individuals and organizations to design reports that precisely align with their data analysis objectives.
This approach empowers users to extract relevant insights, focusing on key metrics, trends, and performance indicators essential to their analytical goals.
How Custom Reporting Works:
The process of custom reporting typically begins with identifying the specific information and insights stakeholders seek to obtain from the data. Users then determine at least three primary criteria for it:
- The key performance indicators (KPIs),
- Metrics, and
- Dimensions critical to their analysis.
Once these parameters are defined, the custom reporting tool or platform is utilized to design and configure reports, specifying the desired data visualizations, formats, and structures.
Core Components of Custom Reporting
While a custom report may constitute different key elements, it is important to note that a custom report typically consists of four critical elements:
- Data Selection: Custom reporting starts with selecting the data sets or sources relevant to the analysis. Users can choose from various data points, databases, or systems based on their informational needs.
- Visualization Elements: Users can decide on the visual representation of data, choosing from a range of chart types, graphs, tables, and other visualization elements. This flexibility allows for a more intuitive and effective communication of insights.
- Data Filters and Parameters: Custom reports often incorporate filters and parameters that enable users to focus on specific subsets of data. This ensures that reports are dynamic and adaptable to evolving analytical requirements.
- Interactive Features: Many custom reporting tools offer interactive features, allowing users to explore data dynamically. This may include drill-down options, hover-over details, and clickable elements for a more detailed analysis.
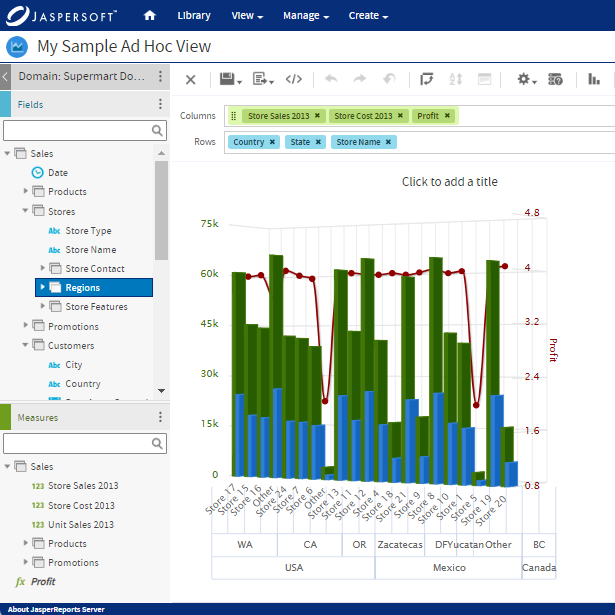
Comparing Custom Reporting to Other Forms of Reporting
When exploring what is custom reporting or understanding the reporting options that an organization has, it is important to understand how custom reporting differs from other forms of reporting. Custom reporting is often compared to standard reporting and ad-hoc reporting.
1. Standard Reporting:
Standard reporting involves the use of pre-built or templated reports that provide a fixed set of data visualizations and metrics. These reports are often designed to address common reporting needs across a broad audience. The key characteristics of standard reporting include:
Fixed Templates: Standard reports follow predetermined templates with limited flexibility.
Static Content: The content of standard reports remains static, offering a consistent view of data.
Broad Applicability: Suitable for general reporting needs applicable to a wide audience.
2. Ad-Hoc Reporting:
Ad-hoc reporting refers to the creation of reports on-the-fly to address immediate and specific data analysis requirements. Users can generate these reports without relying on predefined templates.
Key characteristics that set ad-hoc reporting apart include:
On-Demand Creation: Ad-hoc reports are created as needed, allowing for quick responses to emerging analytical needs.
User-Driven: Users have more control over the structure, content, and visualizations in ad-hoc reports.
Less Standardization: Since ad-hoc reports are created dynamically, there may be less standardization across reports.
3. Custom Reporting:
Custom reporting involves the creation and configuration of reports tailored to meet specific data analysis requirements. Users can define the structure, content, and visual elements to align with their informational needs.
As discussed, custom reporting often differentiates itself with the following characteristics:
Tailored Reports: Reports are highly tailored to address specific informational needs, emphasizing key metrics and trends.
Flexibility: Users have significant flexibility in choosing visualizations, data sources, and report structures.
Precision: Custom reporting provides a precise and focused view of data, avoiding unnecessary details.
Here's a table comparing these three types of reporting:
| Aspect | Standard Reporting | Ad-Hoc Reporting | Custom Reporting |
|---|---|---|---|
Flexibility |
Limited, follows fixed templates. |
Moderate, allows dynamic report creation. |
High, offers extensive customization. |
Template Structure |
Fixed and standardized templates. |
Variable, depending on user requirements. |
Tailored to meet specific needs. |
Content Dynamism |
Static content with minimal dynamism. |
Dynamic content based on immediate needs. |
Dynamic content with precision. |
User Control |
Limited control over report structure. |
More user control over report elements. |
Extensive user control for customization. |
Applicability |
Broad applicability to a wide audience. |
Suitable for specific and immediate needs. |
Tailored to meet specific user requirements. |
When deciding on the most suitable reporting approach, organizations should consider the nature of their data, the diversity of reporting needs, and the level of customization required. Custom reporting stands out for its precision, flexibility, and ability to address unique analytical objectives.
Applications of Custom Reporting
Custom reporting finds wide-ranging applications across various industries and sectors due to its tailored and precise nature. Here are some key applications of custom reporting:
1. Business Performance Analysis:
Custom reporting is extensively used to assess and analyze overall business performance. Organizations can create reports that focus on key performance indicators (KPIs), allowing stakeholders to gain insights into areas such as sales, revenue, and operational efficiency.
2. Marketing and Campaign Analytics:
In the world of marketing, custom reporting aids in evaluating the effectiveness of campaigns and strategies. Marketers can generate reports that highlight crucial metrics like conversion rates, click-through rates, and customer engagement, providing valuable insights for optimizing future campaigns.
3. Financial Reporting and Analysis:
For financial professionals, custom reporting is instrumental in financial analysis and reporting. Reports can be tailored to showcase financial statements, budgetary allocations, and expenditure details, enabling accurate financial decision-making.
4. Human Resources Metrics:
Custom reporting supports human resources by providing in-depth insights into workforce metrics. This includes reports on employee performance, turnover rates, training effectiveness, and diversity metrics, aiding HR professionals in strategic workforce management.
5. Sales & Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
In sales and CRM, custom reports help track and analyze sales performance, customer interactions, and pipeline progression. Organizations can design reports that focus on specific sales territories, product lines, or customer segments to enhance decision-making in sales strategies.
6. Operational Efficiency Monitoring:
Custom reporting is utilized to monitor and enhance operational efficiency within an organization. This includes reports on production processes, supply chain management, and resource utilization, providing insights for streamlining operations.
7. Risk Management & Compliance:
For industries with stringent regulatory requirements, custom reporting is crucial for risk management and compliance. Reports can be customized to showcase adherence to regulations, identify potential risks, and provide detailed compliance documentation.
8. Customer Experience Evaluation:
Custom reports play a critical role in evaluating and improving customer experience. Businesses can create reports that analyze customer feedback, satisfaction scores, and support interactions, contributing to the enhancement of overall customer satisfaction.
9. Strategic Decision-Making:
Ultimately, custom reporting supports decision-making across various business functions. By providing tailored insights, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their specific goals and objectives.
10. Project Management and Progress Tracking:
In project management, custom reports are valuable for tracking project progress, resource allocation, and milestone achievements. Project managers can design reports that provide a comprehensive overview of project status and key performance metrics.
Custom reporting's adaptability and precision make it an indispensable tool across diverse sectors, empowering organizations to harness their data for decision-making and improved performance.
Types of Custom Reports
The word “custom” suggests that custom reports can have extensive variations depending on its intended use. Here is an overview of some custom report types out there.
1. Executive Summary Reports:
Executive summary reports distill comprehensive data into succinct overviews tailored for senior management. These reports focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) and essential metrics, offering high-level insights for executives.
Through clear visualizations and concise summaries, executive summary reports empower leaders to make informed decisions swiftly without getting bogged down by excessive details.
2. Operational Dashboards:
Operational dashboards are dynamic, real-time reporting tools that visually present critical data on a single screen. These customizable dashboards consolidate various metrics, providing a holistic view of operational performance.
By allowing users to interact with the data, operational dashboards empower organizations to monitor and respond to changes promptly. This type of custom report is instrumental in enhancing operational efficiency and aligning teams with strategic goals.
3. Financial Statements:
Custom financial reports cater to the specific needs of finance professionals, offering a detailed analysis of an organization's financial health. These reports include comprehensive financial statements such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
Customization allows financial reports to focus on particular financial aspects, facilitating accurate and targeted financial analysis crucial for decision-making and planning.
4. Sales Performance Reports:
Sales performance reports are customized to evaluate the effectiveness of sales teams, products, or geographical regions. These reports encompass various metrics, including sales revenue, conversion rates, and customer acquisition costs.
Tailored insights from sales performance reports guide sales managers in making better decisions, optimizing resource allocation, and improving overall sales efficiency.
5. Marketing ROI Reports:
Marketing return on investment (ROI) reports assess the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and initiatives. Customized to specific marketing goals, these reports include metrics like customer acquisition cost, conversion rates, and revenue generated.
6. Customer Satisfaction Reports:
Customer satisfaction reports focus on gathering and analyzing customer feedback to measure and enhance overall satisfaction. These reports may include surveys, Net Promoter Scores (NPS), and metrics related to customer support interactions.
Customized customer satisfaction reports help businesses understand customer preferences, identify areas for improvement, and enhance the overall customer experience.
7. Employee Performance Reports:
Custom reports in human resources assess employee performance, training effectiveness, and workforce demographics. These reports aid HR professionals in strategic human resource management by identifying areas for skill development, performance improvement, and talent optimization.
Employee performance reports contribute to informed decision-making in HR strategies.
8. Supply Chain & Logistics Reports:
Custom reports in supply chain and logistics track key performance indicators related to inventory management, order fulfillment, and transportation efficiency. These reports provide valuable insights for optimizing supply chain processes, improving efficiency, and mitigating risks.
Customization allows organizations to focus on specific aspects of the supply chain that are crucial to their operations.
9. Compliance & Regulatory Reports:
Industries subject to regulatory requirements use custom reports for compliance documentation. These reports detail adherence to regulations, potential risks, and actions taken to ensure compliance.
Customized compliance and regulatory reports are essential for demonstrating transparency, mitigating risks, and maintaining adherence to industry standards.
10. Project Status Reports:
Project status reports are customized for project managers to track progress, resource allocation, and milestones. These reports offer a comprehensive overview of project status, helping teams stay on track and meet objectives.
Customization allows project managers to focus on specific project metrics. This, in turn, facilitates effective communication and decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
11. Social Media Analytics Reports:
For businesses active on social media, custom reports analyze metrics such as engagement, reach, and audience demographics. These reports provide insights into the effectiveness of social media campaigns, identify successful strategies, and highlight areas for improvement. Customization ensures that social media analytics reports align with specific marketing goals and objectives.
12. Quality Assurance Reports:
Custom reports in quality assurance assess product or service quality by tracking defects, testing outcomes, and customer complaints. These reports contribute to continuous improvement processes by identifying areas for enhancement and ensuring product or service quality meets or exceeds standards.
13. IT Performance Reports:
Information technology teams utilize custom reports to monitor system performance, network efficiency, and cybersecurity metrics. These reports support proactive IT management and troubleshooting by providing insights into key IT performance indicators.
Customized IT performance reports allow IT professionals to tailor reports to their specific monitoring needs, ensuring effective management of IT resources and infrastructure.
This list isn't exhaustive, showcasing how custom reports are indispensable tools that cater to the specific informational needs of organizations across various functions. By providing targeted insights and actionable intelligence, these reports empower users to make informed decisions, optimize strategies, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
The flexibility of custom reporting ensures adaptability to evolving requirements, making it a valuable asset for organizations in today's data-driven landscape.

Considerations When Implementing Custom Reporting Solutions
Implementing custom reporting solutions requires a thoughtful approach to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of the reporting process. Consider the following key factors during the implementation phase:
Define Clear Objectives: Clearly articulate the objectives of implementing custom reporting solutions. Understand the specific informational needs and goals that the reports aim to address. This clarity ensures that the reports align with the strategic priorities of the organization.
User Involvement and Feedback: Involve end-users, stakeholders, and decision-makers in the design and customization process. Gather feedback to understand their reporting requirements and preferences. User involvement enhances the relevance and usability of the reports, promoting better adoption across the organization.
Data Quality and Consistency: Ensure the integrity and quality of the underlying data. Inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to unreliable insights. Implement data validation processes, cleansing procedures, and regular audits to maintain data accuracy and reliability.
Scalability: Anticipate future growth and scalability requirements. Custom reporting solutions should accommodate increasing data volumes and evolving business needs. Scalability ensures that the reporting system remains effective and responsive as the organization expands.
Integration with Existing Systems: Assess the compatibility and integration capabilities of custom reporting solutions with existing software and data infrastructure. Seamless integration minimizes disruptions and allows for a unified data ecosystem, preventing silos and enhancing overall data accessibility.
Security Measures: Prioritize data security and implement robust measures to protect sensitive information. This includes user authentication, authorization controls, encryption, and adherence to data privacy regulations. A secure reporting system instills confidence in users and safeguards organizational data.
Customization Flexibility: Choose reporting solutions that offer a high degree of customization flexibility. The ability to tailor reports to specific requirements ensures that the reports deliver the right insights to the right stakeholders. Customization flexibility also supports adaptability to changing business needs.
User Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training for end-users to maximize the utilization of custom reporting tools. A well-trained user base enhances the effectiveness of reporting solutions and encourages widespread adoption. Additionally, establish a support system to address user queries and issues promptly.
Performance Optimization: Optimize the performance of custom reporting solutions to deliver timely insights. This includes optimizing queries, minimizing load times, and employing caching mechanisms. Efficient performance ensures that users can access and analyze data without unnecessary delays.
Governance and Standardization: Establish governance policies and standardized practices for custom reporting. Define data standards, naming conventions, and reporting protocols to maintain consistency across reports. Governance ensures that reporting processes adhere to organizational standards and best practices.
Cost Considerations: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including initial setup, maintenance, and potential scalability costs. Understand the licensing model of the reporting solution and consider the long-term financial implications. A thorough cost analysis helps in making informed decisions about the selected reporting solution.
Adaptability to Changing Requirements: Choose reporting solutions that can adapt to evolving business requirements and technological advancements. Flexibility in adapting to new data sources, analytics techniques, and reporting formats ensures that the reporting system remains relevant over time.
These considerations are designed to help organizations implement custom reporting solutions that align with their strategic objectives, provide actionable insights, and contribute to informed decision-making across various functional areas.
Conclusion
Implementing custom reporting solutions demands careful consideration of key factors, ranging from defining clear objectives and ensuring data quality to addressing scalability, integration, and security. These considerations collectively contribute to the successful implementation of custom reporting solutions, fostering a data-driven culture within organizations.
In a world driven by data, the transformative potential of custom reporting lies in its ability to provide targeted insights, promote strategic decision-making, and enhance operational efficiency across diverse sectors. As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of data analysis, custom reporting remains an invaluable asset, enabling them to unlock the full potential of their data and navigate the path to informed and strategic excellence.
Custom Reporting with Jaspersoft
Related Resources
Jaspersoft in Action: Embedded BI Demo
See everything Jaspersoft has to offer – from creating beautiful data visualizations and dashboards to embedding them into your application.
Back to Basics: Reporting 101
Discover the fundamentals of delivering reporting to users wherever they are and in a variety of formats.
